QRCodes
In this example, we add a robot and start collecting robot data to PostgreSQL and maps and scanned QRcodes to MinIO as image files.
You will also need 2 terminal windows, to:
- Run the Nav2 turtlebot3 launchfile: it starts localization, navigation and RViz
- Run DC
Since RViz is pretty verbose, using 3 terminal windows will help reading the JSON printed on the terminal window.
| Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| RViz | Start it independently because of its verbosity |
| Nav2 | Localization and navigation |
| DC | Data collection |
Setup MinIO and PostgreSQL
MinIO
MinIO will be used as storage for images and other files. To start it, follow the steps
PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL will be used as database storage for our JSON. Later on, backend engineers can make requests on those JSON based on measurement requested and time range. To start it, follow the steps
Setup the ROS environment
In each, terminal, source your environment and setup turtlebot configuration:
source /opt/ros/humble/setup.bash
source install/setup.bash
export GAZEBO_MODEL_PATH=$GAZEBO_MODEL_PATH:/opt/ros/humble/share/turtlebot3_gazebo/models
export GAZEBO_MODEL_PATH=$GAZEBO_MODEL_PATH:/opt/ros/humble/share/aws_robomaker_small_warehouse_world/models/
export TURTLEBOT3_MODEL=waffle
Start RVIZ
ros2 run rviz2 rviz2 -d ${PWD}/install/dc_simulation/share/dc_simulation/rviz/qrcodes.rviz
Start Navigation
Then, start the Turtlebot launchfile with custom parameters to start the QRcode world:
ros2 launch nav2_bringup tb3_simulation_launch.py \
headless:=False \
x_pose:="-16.679400" \
y_pose:="-15.300200" \
z_pose:="0.01" \
roll:="0.00" \
pitch:="0.00" \
yaw:="1.570796" \
robot_sdf:="${PWD}/install/dc_simulation/share/dc_simulation/worlds/waffle.model" \
map:="${PWD}/install/dc_simulation/share/dc_simulation/maps/qrcodes.yaml" \
world:="${PWD}/install/dc_simulation/share/dc_simulation/worlds/qrcodes.world" \
nav2_params_file:="${PWD}/install/dc_simulation/share/dc_demos/params/qrcodes_nav.yaml" \
dc_params_file:="${PWD}/install/dc_simulation/share/dc_demos/params/qrcodes_minio_pgsql.yaml" \
rviz_config_file:="${PWD}/install/dc_simulation/share/dc_simulation/rviz/qrcodes.rviz" \
use_rviz:=False
RViz and Gazebo will start: you should now see the robot in Gazebo, and the map on RViz.
Set the robot position using the "2D Pose Estimate" button.
Start DC
Execute
ros2 launch dc_demos tb3_qrcodes_minio_pgsql.launch.py
With this, all data will be transmitted
Understanding the configuration
The full configuration file can be found here.
For this demo, we will reconstruct the yaml configuration element by element, given how large it is. Go through the explanation to understand how it works.
Collect command velocity, position and speed to PostgreSQL as a group
Similarly to the previous tutorial:
destination_server:
ros__parameters:
flb:
flush: 1
flb_grace: 1
log_level: "info"
storage_path: "/var/log/flb-storage/"
storage_sync: "full"
storage_checksum: "off"
storage_backlog_mem_limit: "1M"
scheduler_cap: 200
scheduler_base: 5
http_server: true
http_listen: "0.0.0.0"
http_port: 2020
in_storage_type: "filesystem"
in_storage_pause_on_chunks_overlimit: "off"
destination_plugins: ["flb_pgsql"]
flb_pgsql:
plugin: "dc_destinations/FlbPgSQL"
inputs: ["/dc/group/robot"]
host: "127.0.0.1"
port: 5432
user: fluentbit
password: password
database: "fluentbit"
table: "dc"
timestamp_key: "date"
async: false
time_format: "double"
time_key: "date"
group_server:
ros__parameters:
groups: ["robot"]
robot:
inputs:
[
"/dc/measurement/cmd_vel",
"/dc/measurement/position",
"/dc/measurement/speed",
]
output: "/dc/group/robot"
sync_delay: 5.0
group_key: "robot"
tags: ["flb_pgsql"]
measurement_server:
ros__parameters:
custom_str_params: ["robot_name"]
robot_name: "C3PO"
measurement_plugins: ["cmd_vel", "position", "speed"]
custom_str_params_list: ["robot_name", "id"]
custom_str_params:
robot_name:
name: robot_name
value: "C3PO"
# Requires systemd package
id:
name: id
value_from_file: /etc/machine-id
run_id:
enabled: true
counter: true
counter_path: "$HOME/run_id"
uuid: false
moving:
plugin: "dc_conditions/Moving"
cmd_vel:
plugin: "dc_measurements/CmdVel"
group_key: "cmd_vel"
enable_validator: true
topic_output: "/dc/measurement/cmd_vel"
include_measurement_name: true
position:
plugin: "dc_measurements/Position"
group_key: "position"
topic_output: "/dc/measurement/position"
enable_validator: true
global_frame: "map"
robot_base_frame: "base_link"
transform_timeout: 0.1
include_measurement_name: true
speed:
plugin: "dc_measurements/Speed"
group_key: "speed"
odom_topic: "/odom"
topic_output: "/dc/measurement/speed"
include_measurement_name: true
In the measurement server, we set 3 measurements: cmd_vel, position and speed being collected once per second, are validated with their respective JSON schemas and publish on their own topics.
Note the include_measurement_name which include measurement name in the JSON, which is used when grouping. The group collects the data from those 3 measurement and republishes it on the group topic /dc/group/robot.
In the destination server, we enable the PostgreSQL plugin and configure its credentials.
Be sure to change the login and password to your current infrastructure configuration. Do it in production setup!
You can find more about the PostgreSQL plugin here
To take a look at records, go to Adminer. It is by default started at http://localhost:8080, it is a database GUI.:
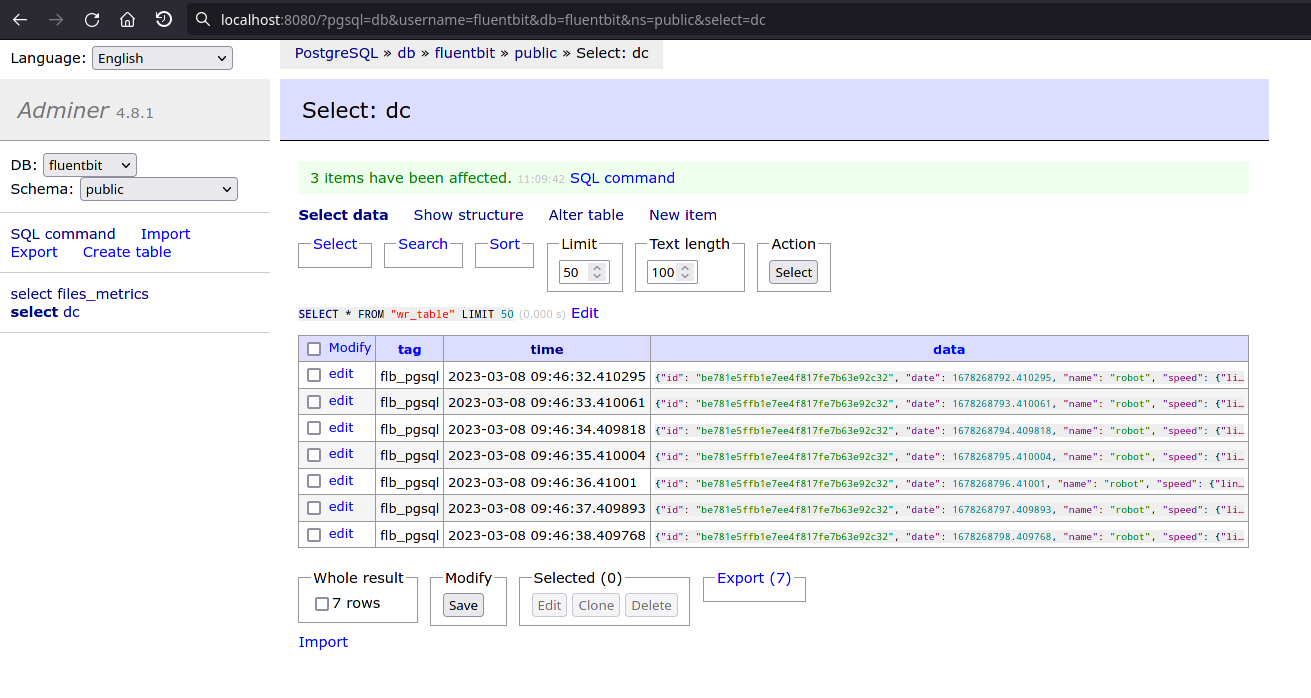
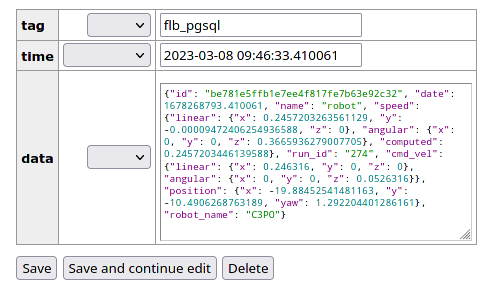
You can then click on a record, to take a look, edit or delete it:
Send the map image and YAML from nav2_map_server to MinIO
First, we add the map measurement. We use 3 plugins here: flb_pgsql to send the data to PostgreSQL on the dc database, then flb_minio to send some files to MinIO and flb_files_metrics which will be used to autodelete the files once they reach their destination.
measurement_server:
ros__parameters:
...
measurement_plugins: ["map"]
map:
plugin: "dc_measurements/Map"
group_key: "map"
polling_interval: 5000
save_path: "map/%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S"
topic_output: "/dc/measurement/map"
save_map_timeout: 4.0
remote_prefixes: [""]
remote_keys: ["minio"]
enable_validator: true
tags: ["flb_pgsql", "flb_minio", "flb_files_metrics"]
include_measurement_name: true
...
Then we add the destinations:
destination_server:
ros__parameters:
...
destination_plugins: ["flb_files_metrics", "flb_pgsql", "flb_minio"]
flb_files_metrics:
plugin: "dc_destinations/FlbFilesMetrics"
inputs: ["/dc/measurement/map"]
file_storage: ["minio"]
db_type: "pgsql"
delete_when_sent: true
minio:
endpoint: 127.0.0.1:9000
access_key_id: rQXPf1f730Yuu2yW # Change it
secret_access_key: TYYkjN5L4gqDgCGLzQahHDcvqL4WNTcb # Change it
use_ssl: false
bucket: "mybucket"
src_fields: ["local_paths.pgm", "local_paths.yaml"]
upload_fields: ["remote_paths.minio.pgm", "remote_paths.minio.yaml"]
input_names: ["map", "map"]
pgsql:
host: "127.0.0.1"
port: "5432"
user: fluentbit # Change it
password: password # Change it
database: "fluentbit"
table: "files_metrics"
timestamp_key: "date"
time_format: "double"
time_key: "date"
ssl: false
flb_minio:
verbose_plugin: false
time_format: "iso8601"
plugin: "dc_destinations/FlbMinIO"
inputs: ["/dc/measurement/map"]
endpoint: 127.0.0.1:9000
access_key_id: rQXPf1f730Yuu2yW # Change it
secret_access_key: TYYkjN5L4gqDgCGLzQahHDcvqL4WNTcb # Change it
use_ssl: false
create_bucket: true
bucket: "mybucket" # Change it
src_fields: ["local_paths.pgm", "local_paths.yaml"]
upload_fields: ["remote_paths.minio.pgm", "remote_paths.minio.yaml"]
flb_pgsql:
plugin: "dc_destinations/FlbPgSQL"
inputs: ["/dc/group/map"]
host: "127.0.0.1"
port: 5432
user: fluentbit
password: password
database: "fluentbit"
table: "dc"
timestamp_key: "date"
async: false
time_format: "double"
time_key: "date"
This will save the map pgm and yaml every 5 seconds to MinIO. Head to the MinIO GUI, which is by default located at http://localhost:9001. Default user/password are minioadmin/minioadmin.
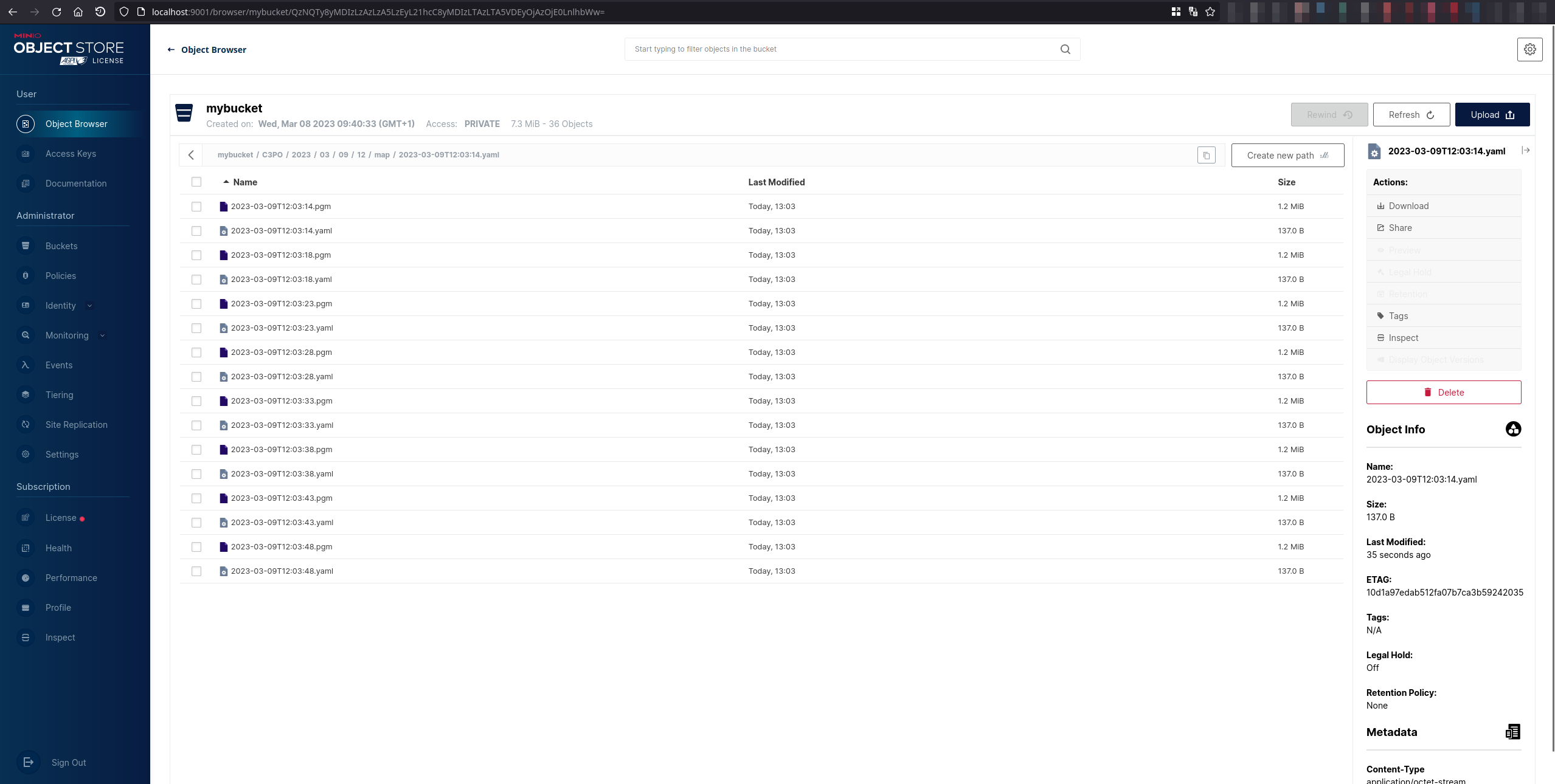
It will also save the map metadata on PostgreSQL, which you can later use to know the map location on MinIO and its dimensions for example:
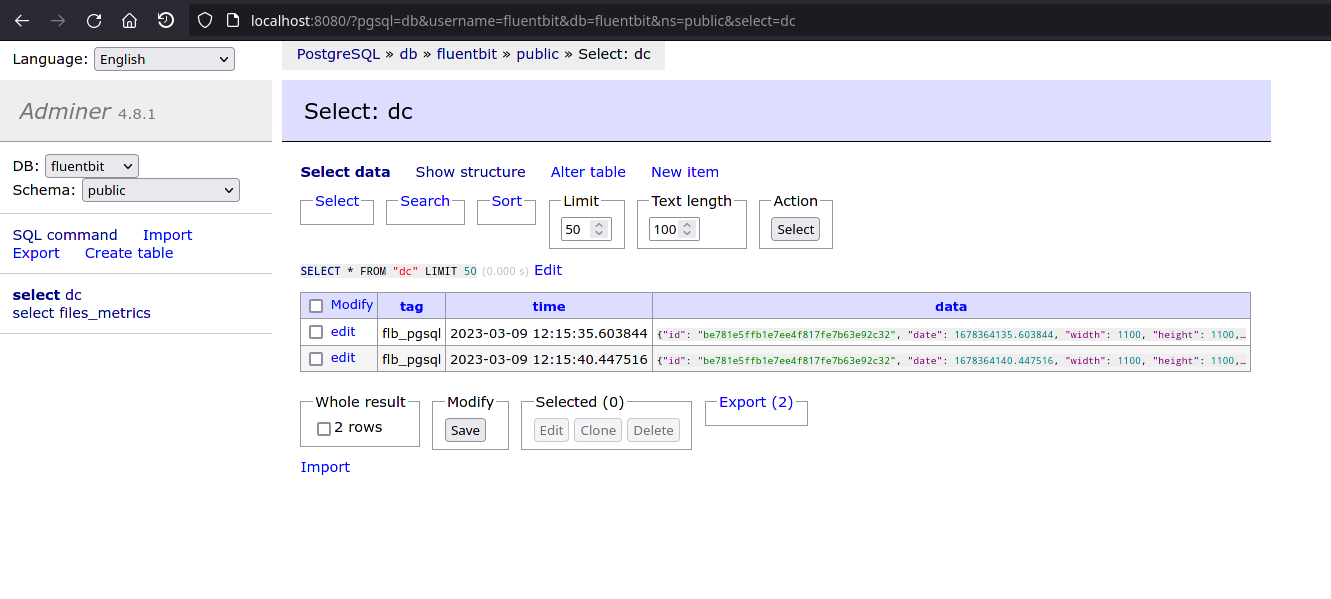
We also transmit the metadata, to be fetched later on by the backend (map dimension and path). It is set in the flb_pgsql measurement plugin.
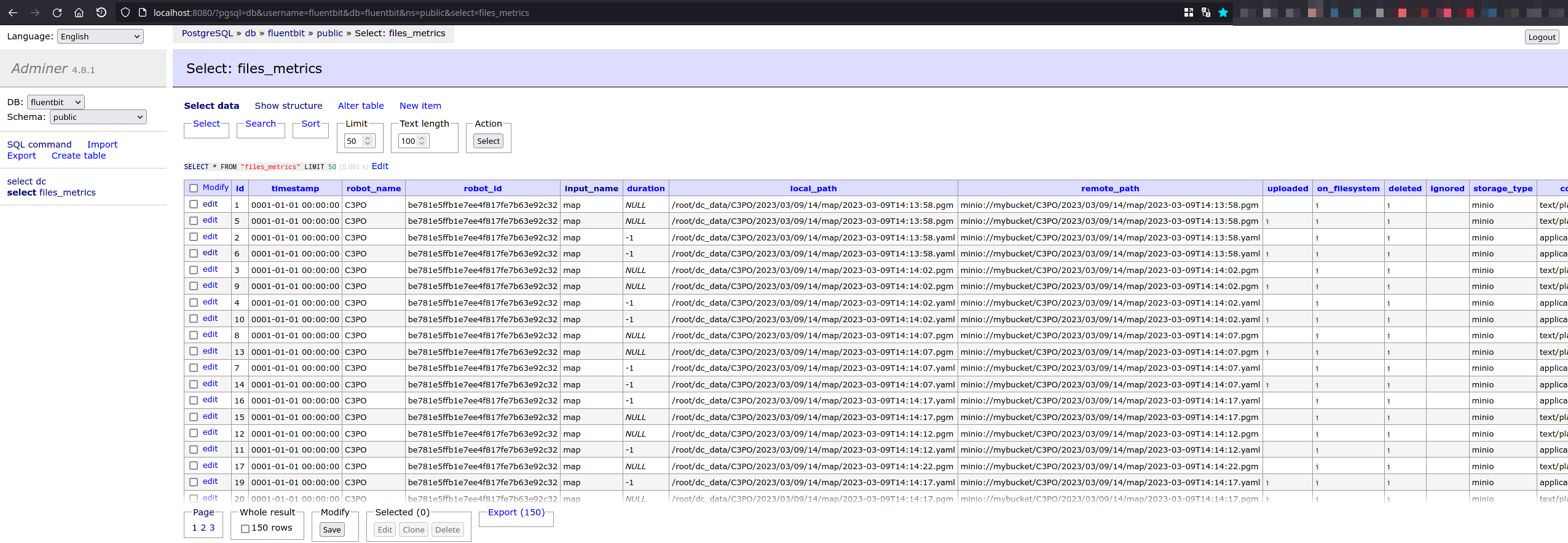
The flb_metrics plugin is also enabled. We use it to track if the file is on the filesystem and also delete it once it reaches its destination, here MinIO. This plugins deletes file when they are sent with the delete_when_sent parameter. More about the plugin here
Then, similarly, on Adminer, you can check the data is uploaded and deleted:
Send QR code images to MinIO
We want to collect pictures taken by the cameras
measurement_server:
ros__parameters:
...
measurement_plugins: ["right_camera", "left_camera"]
condition_plugins: ["moving", "inspected_exists"]
custom_str_params_list: ["robot_name", "id"]
custom_str_params:
robot_name:
name: robot_name
value: "C3PO"
# Requires systemd package
id:
name: id
value_from_file: /etc/machine-id
run_id:
enabled: true
counter: true
counter_path: "$HOME/run_id"
uuid: false
destinations:
minio:
bucket: mybucket
moving:
plugin: "dc_conditions/Moving"
inspected_exists:
plugin: "dc_conditions/Exist"
key: "inspected"
right_camera:
plugin: "dc_measurements/Camera"
group_key: "right_camera"
if_none_conditions: ["moving"]
if_all_conditions: ["inspected_exists"]
topic_output: "/dc/measurement/right_camera"
init_collect: false
init_max_measurements: -1
condition_max_measurements: 1
node_name: "dc_measurement_camera"
cam_topic: "/right_intel_realsense_r200_depth/image_raw"
cam_name: right_camera
enable_validator: true
draw_det_barcodes: true
save_raw_img: false
save_rotated_img: false
save_detections_img: true
save_inspected_path: "right_camera/inspected/%Y-%m-%dT%H-%M-%S"
rotation_angle: 0
detection_modules: ["barcode"]
remote_prefixes: [""]
remote_keys: ["minio"]
tags: ["flb_pgsql", "flb_minio", "flb_files_metrics"]
include_measurement_name: true
left_camera:
plugin: "dc_measurements/Camera"
group_key: "left_camera"
if_none_conditions: ["moving"]
if_all_conditions: ["inspected_exists"]
topic_output: "/dc/measurement/left_camera"
init_collect: true
init_max_measurements: -1
condition_max_measurements: 1
node_name: "dc_measurement_camera"
cam_topic: "/left_intel_realsense_r200_depth/image_raw"
cam_name: left_camera
enable_validator: true
draw_det_barcodes: true
save_raw_img: false
save_rotated_img: false
save_detections_img: true
save_inspected_path: "left_camera/inspected/%Y-%m-%dT%H-%M-%S"
rotation_angle: 0
detection_modules: ["barcode"]
remote_prefixes: [""]
remote_keys: ["minio"]
tags: ["flb_pgsql", "flb_minio", "flb_files_metrics"]
include_measurement_name: true
...
Taking a look at the cameras, we can understand that:
- Data is only collected when the robot is not moving:
if_none_conditions: ["moving"] - Data is only collected when there is inspected data, so only when a QR code is detected:
if_all_conditions: ["inspected_exists"] - Data is not collected constantly:
init_max_measurements: -1 - Only one record is collected when conditions are triggered:
condition_max_measurements: 1 - Only images with inspected data are collected:
save_raw_img: falsesave_rotated_img: falsesave_detections_img: true
- Barcodes are scanned in each image:
detection_modules: ["barcode"]
For the files-metrics, it is very important to have include_measurement_name since it relies on it to know in which field needs the paths are.
Then we add the destination:
destination_server:
ros__parameters:
...
destination_plugins: ["flb_minio", "flb_pgsql", "flb_files_metrics"]
flb_files_metrics:
plugin: "dc_destinations/FlbFilesMetrics"
inputs:
[
"/dc/measurement/right_camera",
"/dc/measurement/left_camera",
]
file_storage: ["minio"]
db_type: "pgsql"
delete_when_sent: true
minio:
endpoint: 127.0.0.1:9000
access_key_id: rQXPf1f730Yuu2yW
secret_access_key: TYYkjN5L4gqDgCGLzQahHDcvqL4WNTcb
use_ssl: false
bucket: "mybucket"
src_fields:
[
"local_paths.inspected",
"local_paths.inspected"
]
upload_fields:
[
"remote_paths.minio.inspected",
"remote_paths.minio.inspected"
]
pgsql:
host: "127.0.0.1"
port: "5432"
user: fluentbit
password: password
database: "fluentbit"
table: "files_metrics"
timestamp_key: "date"
time_format: "double"
time_key: "date"
ssl: false
flb_minio:
verbose_plugin: false
time_format: "iso8601"
plugin: "dc_destinations/FlbMinIO"
inputs: ["/dc/measurement/right_camera", "/dc/measurement/left_camera"]
endpoint: 127.0.0.1:9000
access_key_id: rQXPf1f730Yuu2yW
secret_access_key: TYYkjN5L4gqDgCGLzQahHDcvqL4WNTcb
use_ssl: false
bucket: "mybucket"
src_fields:
[
"local_paths.inspected",
"local_paths.inspected"
]
upload_fields:
[
"remote_paths.minio.inspected",
"remote_paths.minio.inspected"
]
flb_pgsql:
plugin: "dc_destinations/FlbPgSQL"
inputs:
[
"/dc/measurement/right_camera",
"/dc/measurement/left_camera",
]
host: "127.0.0.1"
port: 5432
user: fluentbit
password: password
database: "fluentbit"
table: "dc"
timestamp_key: "date"
async: false
time_format: "double"
time_key: "date"
Here, we collect images with the MinIO plugin, also send metadata to PostreSQL.
In addition, flb_files_metrics tracks when the files are sent to MinIO and deletes them when it is done. Note that multiple destinations can be configured for each field. Check the plugin documentation to see which remote destinations are supported.